Table Of Content

As the first blade pulls the hair up, the next blades cut the hair in a way that causes the hair to go back into the skin after shaving. Digging into the skin to pull the hair out can cause an infection. Also, people should wear loose clothing on areas surrounding the hair to avoid friction. Ingrown hairs are irritating, but most of the time they can easily be treated in the home. Doctors treat staph infections with antibiotics to prevent other serious complications, such as a blood infection. If bacteria, fungi, or other pathogens enter the skin, an infection can develop, known as folliculitis.
How is ingrown hair diagnosed?
Cutting hair very close to the skin creates a very sharp tip on the end of each of the hairs. A doctor will usually assess an ingrown hair infection by looking at the symptoms and asking about your medical history. Ingrown hairs are most common in areas of hair removal, such as the face, legs, armpits, and pubic region.
Best for Sensitive Skin
Some OTC products may help coax the hair up and out of the skin, which may reduce the risk of infection. In this article, we describe how to safely remove ingrown hair on the legs and prevent the issue from recurring. If the bumps or cysts become extremely bothersome — or if they aren’t fading — see a healthcare professional or dermatologist. Prescription acne medications might be needed if OTC methods don’t work. For example, a healthcare professional may prescribe a steroid cream such as hydrocortisone to help reduce redness and pain around your bump or cyst. The hair grows from the bottom of your pore and is kept bathed in sebum secreted by the pore.
Use the razor on your pubic hair only.
They may appear anywhere hair grows on your body, but they commonly appear in places where you shave, tweeze or wax, especially your face, legs, armpits and pubic area. A good skin care routine helps prevent ingrown hairs from forming, while at-home treatments can help release the hair from underneath your skin and provide relief. Contact your healthcare provider if you notice any signs of infection.

These unsightly bumps can be an annoying side effect of hair removal. The good news is ingrown hairs can be treated effectively at home. Hair removal creams dissolve the hair and will leave the ends of the hair softer, rather than sharp. But you should wait to use the creams until your skin has fully healed, as it can cause additional irritation.
I Switched to a Single-Blade Razor. Here's What Happened - Men's Health
I Switched to a Single-Blade Razor. Here's What Happened.
Posted: Fri, 21 Jul 2017 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Exfoliating scrubs can reduce dead skin cells, and allow the surface of the skin to easily pass hairs. Retin-A can further remove dead skin cells and help correct pigmentation that occurs from the ingrown hair. Antibiotics can be administered to fight infection and reduce swelling.
How often should you oil your hair?
There are some OTC creams and treatments available for people who regularly get ingrown hairs. Razor bumps and ingrown hair cysts can take several days or even weeks to fully clear up on their own. Timely treatment can help get rid of them and prevent them from returning. If you want to shave, or remove hair in another way, there are things you can do to prevent ingrown hairs and help them get better quicker.
How is an ingrown hair treated?
While this gel is marketed towards men, all genders would benefit from applying this product before shaving to prevent pesky in-grown hairs. The gel is also unscented so despite it being targeted at men, women could also enjoy the benefits of applying this product before shaving. If they’re not infected, some ingrown hair cysts can go away on their own.
Docs Tell Woman She Has 'Ingrown Hair' But Pain Was Breast Cancer - SurvivorNet
Docs Tell Woman She Has 'Ingrown Hair' But Pain Was Breast Cancer.
Posted: Mon, 27 Mar 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Or, you can take preventative steps like shaving differently or using a razor with just one blade. While ingrown hairs can develop in places all over the body, one of the most common trouble spots, especially for people who shave their facial areas, are ingrown hairs on the face. Ingrown hairs can commonly develop after shaving facial hair and an effective treatment needs to be able to exfoliate dead skin cells as well as reduce razor bumps and redness. As far as we know, dandruff doesn't necessarily directly cause hair loss.
First, “leaving hair oil on for too long can lead to occlusion of the follicles and can contribute to seborrheic dermatitis,” says Dr. Spann. So, if you sleep with it overnight, make sure to wash yours out after 8 to 10 hours with shampoo. And if you notice your scalp starts to feel irritated, flaky, or itchy—aka the opposite of how you want your scalp to feel after oiling—stop oiling ASAP and make an appointment with your dermatologist. If you don’t have the patience to leave it overnight—or your scalp tends to be oil-prone—try hair oiling as a pre-shampoo treatment.
It can be used in the shower (just before adding conditioner) or applied to damp skin right after getting out of the shower. It is recommended to apply a quarter-size amount to the impacted area and rub it into the skin in a circular motion. While you should use this product as needed, be aware that overuse (without a moisturizing conditioner) can dry out the scalp. Mixing tea tree, coconut, and tamanu oils, the Fur Ingrown Concentrate can calm redness and is gentle enough on the skin that you can apply it anywhere on your body—especially on more sensitive areas. It only requires a few drops to the affected area as needed or you can help exfoliate the area with the included finger mitt.
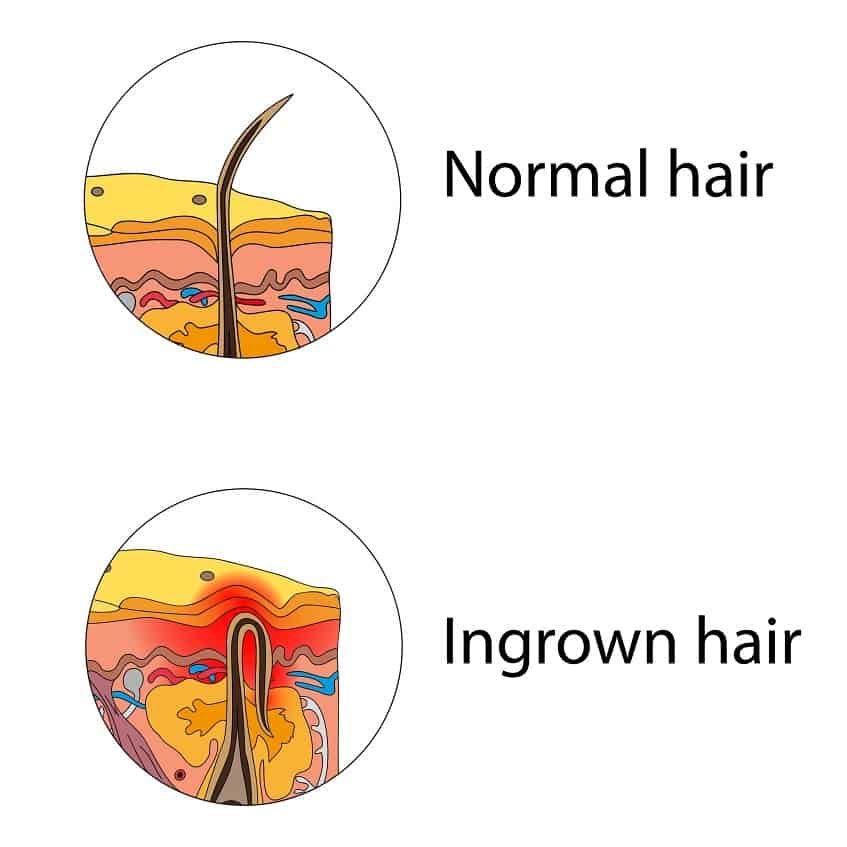
Shaving and waxing creates sharper hairs that tend to get trapped in the skin. Keep reading to learn how to recognize an infected ingrown hair, as well as tips for treating and preventing them. An infected ingrown hair happens when a hair is blocked from leaving the skin or newly emerged hair curls back into the skin, and the follicle becomes infected.
When you have thick or curly hair, you can get a type of ingrown hair called pseudofolliculitis. The hair that grows back has a sharper edge, so it can more easily poke back through your skin and get trapped under the surface. Sometimes, dead skin can clog a hair follicle, which forces the hair to grow sideways under your skin rather than up and out. If you cut naturally curly hair too short, the sharpened end of the hair can pierce your skin, causing an ingrown hair.
Sometimes ingrown hairs are irritating to deal with or become a regular problem. When this happens, some people stop removing hair in the problem area altogether. These simple practices are often enough to make the ingrown hairs go away on their own. When a hair grows to about 10 millimeters in length, it will usually release itself from the follicle. The most common cause of ingrown hairs is an improper shaving technique.
No comments:
Post a Comment